Zellular Sequencer
Zellular is a decentralized sequencer that enables developing high-throughput dApps implemented in high-level languages like JS, Python, and Go. These dApps can be decentralized as Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) services, replicated and secured on EigenLayer and other restaking platforms.
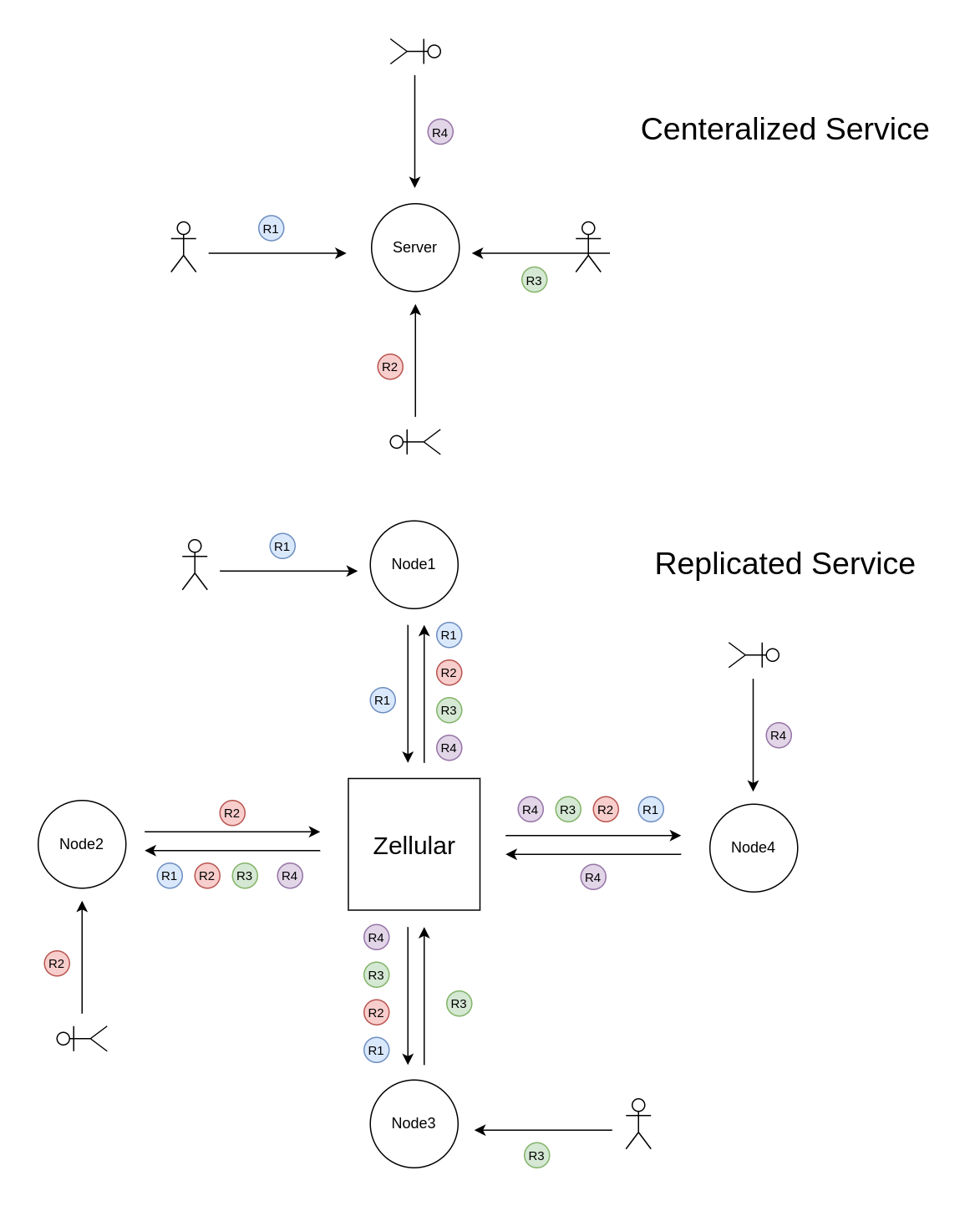
High-throughput dApps need to manage a large volume of user interactions, such as transactions or updates, which need to be processed quickly and consistently. In a decentralized environment, these requests are no longer directed to a single server but must be propagated across all replicas of the service in the exact same sequence to ensure consistency among the nodes. Zellular acts as a decentralized, high-performance messaging system, ensuring that updates are propagated and applied in the same order across all nodes, preserving database uniformity.
Note
This project is under active development and should not be used in production yet.